Disciplinary Procedures – Hotel HR Planning & Development
Disciplinary procedures is an important part in an organization. It is necessary for the employees to obey the rules, codes and policies laid by the organization.
Aspects which shape an employee’s workplace behaviour:
- Family: the inculcation of respect for adult and parental authority encourages us to generally respect authority.
- Institutional setting: in school, university and work we learn how to function in an organization, often accepting our subordinate position.
- Rewards: compliance brings rewards, disobedience brings punishment.
- Perception of authority: authority is normally supported, so we are generally predisposed to follow organizational and managerial rules, but where this does not happen, the organization may have to take disciplinary action.
A good disciplinary procedures should:
- Be in writing.
- Specify to whom they apply.
- Be non-discriminatory.
- Ensure matters are dealt with, without unnecessary delay during Discipline procedures.
- Allow for information about proceedings, witness statements and records to be kept confidential.
- State the disciplinary actions which may be taken.
- Specify the levels of management which have the authority to take the various forms of disciplinary action.
- Provide for employees to be informed of complaints against them and where possible all relevant evidence before any hearing.
- Give employees the opportunity to state their case before a decision is reached.
- Provide employees with the right to be accompanied by a trade union representative or fellow employee at any hearing.
- Ensure that except for gross misconduct, no employee is dismissed for a first breach of discipline.
- Ensure that disciplinary action is not taken until the case has been carefully investigated by management.
- Ensure that employees are given an explanation for any penalty imposed.
- Provide employees with rights to appeal, normally to a senior manager.
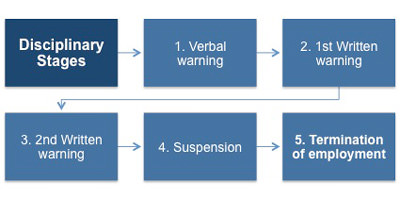
Reasons for Disciplinary Procedures:
- theft or fraud;
- physical violence or bullying;
- deliberate and serious damage to property;
- serious misuse of an organization’s property or name;
- deliberately accessing internet sites containing pornographic, offensive or obscene material;
- serious insubordination;
- unlawful discrimination or harassment;
- bringing the organization into serious disrepute
- serious incapability at work brought on by alcohol or illegal drugs;
- causing loss, damage or injury through serious negligence;
- a serious breach of health and safety rules; and
- a serious breach of confidence.
Reasons for Dismissal
- Lack of capability: this may refer to when employees may encounter difficulties in their performance and struggle to fulfil their responsibilities; alternatively there may also be situations where an employee is unable to do their job due to ill-health.
- Misconduct: this can range from minor to gross misconduct.
- Redundancy: the law in redundancy is quite complex, though in simple terms, a redundancy will arise when a business is closing, a workplace is closing or there is a diminishing need for employees to do particular kinds of work in an organization.
- Statutory bar.
- Some other substantial reason for Discipline procedures
Unfair Reasons for Dismissal with Disciplinary procedures
- Dismissal on grounds of pregnancy or assertion of paternal paternity or adoption leave rights.
- Dismissal on grounds of trade union membership or stating an intention to join a trade union.
- Refusing to work on an off day.
- Dismissal on grounds of actual or proposed trade union activity undertaken at an appropriate time.
- Dismissal resulting from individual’s refusal to join a trade union.
- The dismissal of an employee without going through the required disciplinary procedures.
- Dismissal connected with the transfer in the organization’s ownership.
- Where no reason for dismissal is given without Disciplinary procedures.
- Where the employee has been unfairly selected for redundancy.
- Dismissal on basis of past criminal offence which is spent.
- Unfair dismissal on the basis of sex, race, disability, sexual orientation or religion/beliefs.
- Asserting a statutory right, for example the national minimum wage (NMW).
- ‘Blowing the whistle’ on malpractice in the workplace.
- Refusal to do something on health and safety grounds.
Learn more about Disciplinary Procedures in Hotel Industry ..here…